Does it ever sound like your packaging designer is speaking a different language? Well, in some sense, they are.
Technical packaging terminology can be difficult to understand, even for those in the field for years. If you need to learn about the jargon and terminologies that are commonly used in the packaging industry, this is the guide you need.
Why Are Packaging Definitions Important to Know?
By understanding packaging definitions, you’ll save time, communicate more clearly and effectively with your team, and build a stronger reputation and overall custom packaged product.
The Individuals Who Should Know Packaging Terms
Ultimately, custom packaging and package design takes place within a company or with multiple degrees of external packaging engineering, often requiring support from independent contractors, consultants, vendor evaluations, independent laboratories, contract packagers, total outsourcing, graphic designers, among other disciplines. Here is a list of professional that should know packaging and printing terms to work more efficiently:
- Packaging designers
- Customer service representatives of such companies
- Brand managers
- Packaging technicians
- Material scientists
- Printers and press operators
- Packaging engineers
- Prepress technicians
- Production managers
- Ink technologists
- Finishing technicians
- Packaging consultants
- Quality control and assurance personnel
- Supply chain managers
- Sustainability managers
- Machine operators
- Technical support specialists
- Regulatory compliance officers
- Sales and marketing professionals
- Procurement and purchasing managers
- Product development managers
- Artwork coordinators
- Brand strategists
- Graphic designers working on these projects
- Research and development teams
Without further ado, let’s dig into our complete glossary of packaging definitions from A to Z!
Numerical Terms
0100 In The Industry: The type of sheets and rolls you can use for commercial purposes. It refers to the types that work for only one side.
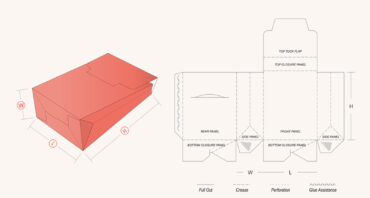
0200 Slotted Boxes: A type of box that is used for packaging purposes. It comes in the form of top and bottom flaps that are stitched or glued.
0201: A standard regular box with outer flaps that meet the top and bottom for sealing.
0300: A type of box with a telescope style and more than one piece alongside a lid.
0500: A type of box that carries several liners or pieces and slides into each other in multiple directions as well.
0900: This jargon is used for treatments that you can add inside your boxes in the form of partitions, pads, and liners. They work as a singular item; you can also glue them as one item.
0700: This type of container has one piece; you would ship them in flat form. At the same time, they are ready-to-use types that need a very easy and simple assembly.
0600: This term is used for rigid style processes that normally have two pieces that are separate. You can switch them together before they are used, and they are known for being large industrial types.
0400: This is another type of folder box and toys that have pieces of box and hinges. At the same time, they come with interlocking tabs.
3PL: Acronym for third-party logistics.
Terms Starting with A
ABS: A logistic that you can create with injection molding and has the ability to give you rigidity and toughness. Although it is a great material that you can use for your packaging, it may be expensive.
Accelerated Test: A test that allows you to find out about the strength of a coating or a box. The main purpose is to test products in shorter intervals that may occur than in real life.
Acid Rain: This refers to a mixture of wet and dry deposition that you can have in that atmosphere. This table is important in the packaging and printing industry as well. Acid rain can cause issues to the sources that help the industry create raw materials for their processes.
Acrylic: A type of thermoplastic material you can get from the polymerization process. So, it is a packaging method that can help you get perfect results for your needs.
Acrylonitrile: That can provide you with transparency, resistance, and rigidity. There are multiple features it can provide in comparison to its alternatives.
Additive: The additive is a type of packaging or printing material that you can use to get a certain result for it.
Adhesive Bleed: It can help you get results against a label material being too pressure sensitive. Multiple scenarios can cause it, like excessive roll winding tension or cold flow.
Aerosol: This term is used for a range of containers that have specific criteria to meet to get this name. One of the features they must contain to have this name is a pressure-resistant container that is also gas-tight. Such a box should also have a desired product.
Aerosol Components: This system is used for liquefied or compressed gasses that you can pack with pressure propulsion containers. This method aims to bring enough pressure to get discharge from a valve.
Aerosol Services: These are filling arousal products that you use as original formulations and can also be customer supplied.
AlphaSeal: This term is used for units that come with the help of getting a folding box board or virgin pulp wood. There are stringent requirements to meet the standards of these products for the food industry. There is a complete range of materials you can use, like aluminum foil.
Alternative Fuels: Fuels used in the packaging industry during shipping and transportation.
Amber Glass: It is a type of brown-colored grass that is used for multiple types of packaging processes. One of the main features of this material is the reduction of light effect on the products packed inside.
Anneal Bubble Pack: A type of temperature process you can use for creating glass products with the use of stresses and strains. You can use natural and uneven cooling for it.
Antioxidant: A type of chemical substance you can use for the purpose of preventing the effects of oxygen on plastic material. Such an oxygen attack can cause brittleness in plastic products and reduces their likability and features.
Anti-Skid Corrugated: A type of corrugated board that comes with chemical treatment and an embossing effect. The benefit of such boxes would be a stable palette and unit load.
Additive: A substance that you can apply to the surface of a plastic product that you can add to it. The main benefit you get from this one is getting rid of electrostatic charges in your products.
Applicator Cap: A type of clay closure that you can add to a packaging box to apply content to them, such as grease spouts or daubers.
Applicator Rod: A type of short glass rod, which comes in the measurement of 2 MM to 4 MM in diameter. You can use it alongside an applicator cap that can help cut a cap.
Assembly: A process in which you combine different box elements into one product. The use of such procedures would be to avoid any contamination inside your box.
AQL: Acronym for the acceptable quality level of a box. This is the maximum percentage move or proportion of a variant In the units that you get with a certain production. The quality assurance department ensures that this variable is under certain guidelines.
Aromatherapy Packaging: These are the items you can use for packaging aromatherapy products which can also be aluminum bottles, candle holders, and others.
Aseptic Packaging: A technique you can use to place a product into a box with sterilization kept in mind. The purpose of this process is completed when you get sterilization for your product and the box. Another benefit you get from this packaging product is that there’s no refrigeration requirement for such products. This also applies when the package seal is broken.
Ampul: A type of smaller container that you can make from glass or plastic tubes. You can draw it into a stem and close it by fusion once you have filled it. You can use a bottom that may be flat and can also draw out as you require it to.
Ampules/Accessories: These are ampules and also accessories that you can find in the form of breakers, sleeves, and others.
AN: A material that comes with rigidity, excellent barrier properties, and transparency. This material is used for thermoforming as well.
Autoclave: A type of pressure vessel that allows you to standardize packages with the help of high-temperature steam or vapor.
Average Wall Thickness: A type of measurement that you find by measuring the thickest section of a box wall and the thinnest one. Then you divide them into two to find out this measurement.
Avoirdupois Weight: A system of weights you can use for the purpose of measuring goods. But you are not supposed to measure precious metals and drugs with this unit.
Animal Healthcare Products in Packaging and Printing: Products that are used for healthcare purposes and come in the packaging category. Injection-molded items are a common example of such packaging products used in the animal health sector.
Aerosol Components: A type of material that is used for the purpose of creating bottles and boxes. For instance, extruded aluminum containers over caps and closures.
Autoclavable: Products you can produce from resins and give you the ability to bear up to 250 degrees of temperature for up to 45 minutes.
Abrasion Resistance: The endurance of a packaging material against scratching and wrapping. This term refers to how strong our packaging material is when it comes to such issues from the use of products that come from them.
Across Flute: This term is used to measure edited materials as it is a unit for their measurement.
A-Flute: A type of corrugated flute that is thickest in their category.
Air Freight: A term used for the products you transport by air. It’s important to have special considerations when packaging such products, such as the sensitivity of the goods, their dimensions, center of gravity, and mass.
Aluminum: A common material for packaging purposes, known for being lightweight and non-toxic.
Allocated Inventory In Packaging: The material quantity that a department has been assigned for their production.
Adhesive: A material that helps bond multiple surfaces into one.
Anaerobic Digestion: Part of biodegradable waste treatment that helps reduce landfill gas emissions into the atmosphere.
Anti-Scuff Bicell: A type of basal sheet that you can use without any woven fabrics. These normally work for the outer surfaces of the item and can help against damage to that product.
Antistat: An anti-static type of packaging that helps avoid any static current in your packaging. This method can help reduce the chances of product damage due to this issue. The full form of this word is anti-static.
Artwork: This term means the logo or unique design that you can create for your packaging, which are typically associated with specific artwork guidelines.
Automotive: This term is used for cars and similar vehicles that may be considered in the packaging industry.
Astraboard: A type of polypropylene that is used inside cases and is famous for its strength and lightweight.
Attenuate: Reduction of force on products that are sensitive to vibration.
ATA: Abbreviation of an association that promotes the safety of your case and packaging specifications. The basic functionality of this association is to promote the safety of these products during air transit jobs.
Terms Starting with B
Backing Liner: A type of paper material you can use to eliminate surface irregularities in packaging products. At the same time, it has the ability to be resistant to water and carry extra strength.
Banding: This type of machine can help improve the level of security you can have with different items.
Back Off: Loosening a cap that may occur due to improper cap application torque.
Backing Liner: A type of compressible paper material to which you can attach the liner. This paper allows you to get rid of any regulation regularities that may exist on the sealing surface. At the same time, you get better strength, appearance, and resistance against spoiling factors.
Baffle Mark: A type of bottom defect that may occur due to a seam coming between the baffle and the blank mold.
Bag-In-Box: A type of sealed plastic bag that you can find inside a rigid outer box. The most common use of this one is for packing liquid products that can be of different viscosities.
Bags: When we talk about bags, there is a long list of products that you can find in the packaging industry. These can be poly bags, mailing currency, anti-static, and many other types of bags.
Bail: A type of wire handle that allows you to carry a product inside a box. You can weld these two to the opposite sides of boxes to get better results for carrying purposes.
Barrier Material: A term used to classify packaging materials that offer protection for the environment. You can find these materials with the properties of having pores. At the same time, this helps remove passage of microorganisms, which helps prevent contamination in the boxes.
Barex: A type of polymer that you can make out of Acrylonitrile. You can also have methyl acrylate and butadiene in these. You can get impressive gas barrier properties and chemical resistance with these. At the same time, it provides you with a good impact.
Barrels: Barrels are a common type of garden, food, storage, or wine type of containers, which can also be made out of plastic.
Barrier Material: Any type of material that can help reduce the chances of passage of moisture, gas, and other problem-causing factors into the packaging.
Baseline Performance: Standards that industry manufacturers adhere to for comparing the performance of their products.
Bead: A type of narrow and round projection that you can find above or below the surface of a packaging box.
Bent Finish: A type of finished defect that normally has a bent or crooked appearance on it. You can also call it a crooked finish, in short.
Barcode: A type of code that can help packaging and printing professionals to understand different aspects about products. For instance, it can help with the SKUs of the product.
Blown Glass: A term for containers that are created from molten glass. The use of air pressure in this process is a prominent factor that helps create the required shape.
Blushing: Widening or discoloration that may occur in a plastic bottle. The reasons behind this event can be physical or chemically induced phase separation.
Board: A heavy-weight thick sheet of paper that can also be created from other fiber substances.
Boston Round: A style of portal which has the features of a cylindrical shape and roundness. The most common use of this container is in the Pharmaceutical industry.
Beacon: A network of high-growth businesses also famous for their positions.
Blank: A piece of corrugated box that has been prepared for making a box. Normally it is in a cut-and-scored form.
Beers Tray: A type of folding tray that is made of corrugated material. You can find it to have glued corners, and it is quite effective for shipping and storage purposes.
Bevel: A type of edge of container structure that does not have a 90-degree angle to the container.
Bins: Boxes used for the purpose of storage of hardware and small parts. You can find them in the shape of corrugated cardboard and recycled plastic. Also, they are useful for shelving and hanging from panels.
Bioburden: The relative number of microorganisms that you can find for a product at a specific time. This measurement may also apply to the level of microorganisms that you can find in a specific area during air sampling.
Biofuel: A type of fuel that you can get from organic matter and not fossil products.
Bird Swing: An edge oversight defect or a string of glass you can find inside a bottle.
Black Spots: General defect or a small black speck that you may find inside a glass bottle or box in the packaging industry.
Blake: A certain type of style of straight oblong bottle used in the Pharmaceutical industry. You can also call them space savers and wide-mouth packers.
Bicell: A plastic sheet material brand you can consider to be a quality product. You can use it as an alternative to Correx.
Bitmap: A type of digital graphic that is based on pixels normally. They have very large files, and you cannot resize them without losing their quality.
B-Flute: A term that refers to a corrugated flute that has 1/8th of an inch.
Bleached Pulp: A type of pulp that you can get by oxidizing chemicals.
Bott: A term for an Aluminum case manufacturer in the packaging industry.
Blister Packs: Blister packs are a common type of packaging made from transparent molded plastic, providing a tamper-proof solution for sensitive products, such as for medical and pharmaceutical product packaging.
Blisters: Blisters are quite different from a blister pack, as blisters can be inside a glass in the form of a bubble.
Blow Molding: A process that you can use to create plastic containers and bottles. This process also involves molding into two halves of a mold. At the same time, air pressure is used to create mold cavities in products made with this process.
Blow Pin: A part of tooling that you can use for creating hollow objects or containers with the help of the blow molding process. You can consider it a tubular tool that allows air pressure into a container to shape the mold you want.
Biodegradable: A material that can decompose in natural conditions. The factors that degrade it are bacteria and other living organisms.
Blow Molding: A type of process that you can use to mold plastics. There are three main types of this process which are injection, injection stretch, and extrusion molding.
Bondline: A term for structural parts of a packaging product, including the adhesive part.
Board: This term is for a thick type of sheet of paper that comes in different variations. Cardboard, containerboard, and fiberboard are 3 common examples of this type.
Bonding: A process to combine different pieces of foam or plastic. The use of this process allows you to get desired thickness and shape of your packaging products.
Board Grade: The type of rate that you can give to corrugated boards on three different elements.
Branding: Branding is a unique aspect or design found on your packaging boxes – such as a logo, color scheme, pattern, icon, slogan, or symbol – that helps people quickly recognize a specific product or suite of products.
Break Pack: A type of transit container that can be a corrugated case.
Bubble Pack: Type of package used to protect products inside your packaging. The basic mechanism of this pack is to create a cushioning between the product and potential damaging factors.
Bottom Plate: Part of the mold carrying heel radius and helps to push up the box.
Boundary and Scope: These are the two terms you can use for the measurement of project parameters and help define attributes and conditions for them.
Bruise Check: A side effect or edge that may appear on the side of our product.
Bulged Finish: A type of finished effect that may be blown out of shape during the production of a box.
Bung: A type of plug you can use to close a barrel. You can also try using it for closing a drum bunghole.
Burn Line: A type of dark streak of material you can have inside a plastic bottle. It can result in the decomposition of the material.
Butterchipboard: A type of pigmented chipboard popular for having smooth sides. You can use it for laminating aluminum foil and quote it with a release quote.
Buttress Thread: A design of a thread profile that can take certain forms, like a right triangle or a slightly different form.
Brush Marks: A general defect that can be on the side of a box. Such artifacts may also appear on the neck of a packaging box.
Brushes: Common packaging equipment that you can use in multiple activities. For instance, you can use them for cosmetic dental, medical, or other applications.
Terms Starting with C
Capacity: The total volume of space a container can offer for a product that you want to store inside it.
CAD: This term stands for the computer-aided design you can use in the form of electronic design automation. You can create them in the form of interactive engineering drawings with the retrieval and storage processes.
CAM: This term is used for a process in the manufacturing of these products. You can use this one to feed data into machines and manufacture products with this data.
Cap: Cover of a bottle or any packaging that keeps it sealed. Using this part of your packaging ensures that you avoid any type of adulteration into it by keeping it tamper-evident.
Canning Supplies: Terminology for mason jars and closures.
Carboy: A type of bottle or other that you can make out of clay, plastic, or metal. Notable for its ability to contain a capacity of three to 13 gallons, used for shipments of spring water and comparable resources.
Catalyst: A type of chemical substance that can improve a chemical reaction but does not take part in this event.
Cavity: The process of plastic blow molding, which works to provide the body of the container.
Carry on Approved: A type of case you can use to meet the luggage requirements for your airline hand luggage needs.
Chemical Block: This term is used for a form that produces a block of chemical resistance.
Chop Edge: The chopping-edge is the length of the board or the sheet you use for packaging products.
CDA: This type of agreement ensures that different organizations do not disclose certain information about certain commitments.
Coatings: There are several types of specialist coatings that you can use on corrugated boxes. These coatings can help you get different types of benefits like waterproofing, anti-corrosion, and other effects.
Cobb Test: This type of test allows you to understand the total amount of water a certain material has absorbed.
C-Flute: A type of corrugated material that can help you get crush resistance. At the same time, this material can offer great printing properties.
Coldset PVA: This type of adhesive material can become liquid when you heat them to 60 degrees. On the other hand, it will lose fluidity under 20 degrees.
Collapsible: A type of box that you can fold to ensure that you can easily bulk transport them.
Conductive: A type of packaging that can offer protection against static currents.
Corrispring: A type of material you can use as an alternative to foam and polystyrene cushioning often considered for its eco-friendliness.
Corrugator: This term is used for an industrial machine that combines various paper types to create a new type.
Corrust: A special type of coating you can use to avoid cohesion corrosion. Its main uses for protecting metal products for both storage and transit processes.
Corstat: A type of carbon-based coating that you can use for corrugated cardboard. Its ability to get rid of static current makes it important for the packaging and printing industry.
Corstat Container: Boxes, picking bins, and trays that have anti-static coating on them.
CQV: Acronym for commissioning, qualifying, and verifying. These management methods ensure that packaging systems and machinery are kept in the best conditions.
Cradle: Corrugated cardboard inserts and fittings that you can use to protect during shipping.
Corrugated Material: The main feature of this material is its shape which allows you to get a lot of strength and stability against difficult conditions for packaging products. It carries ridges and grooves that can help improve the ability to provide strength.
Corrugated Board Material: The main feature of this material is containing fluted paper sheets.
Containers For Shipping: A type of container that you can use for shipping purposes.
Contract Packaging: A 3rd party packaging company that provides you with human resources and packaging boxes for your business.
Countertop: A type of displacement for retail packaging. You can consider them similar to shelf-ready boxes.
Convertor: Companies that convert raw materials into packaging products.
Copolymer Resin: A type of plastic material that is famous for its flexibility and toughness. At the same time, it has a great ability for transparency and clarity.
Cores: Manufactured from wood pulp fiber, the fibers are wrapped around a rod in a spiral to create a tube shape. For the size of the core, consider both the core’s diameter and length.
Corner Blocks: Corners that you can use for form packaging. The main purpose of peace products is to help reduce the chances of product damage during the shipment process.
Correx: A type of twin-walled plastic that has multiple applications in the packaging industry.
Corriflute: This term is used for Correx plastic material as a second name.
Carton Board: A type of material that is stiffer than a board. You can use it for its ability to avoid compression and moisture issues. It has the ability to resist both of these issues.
Closed Loop System: This term is used for an industrial system that carries zero waste and can reuse and recycle all the materials it uses for production. It can even do the composting processes to improve the eco-friendliness of your methods.
CNC Routing: A process that allows for the usage of different materials. The main benefit of this method is the use of computerized devices.
Closures: A type of device or technique that you can use for sealing packaging boxes. There are some common techniques for this purpose, like stapling, glowing, and tapping.
Case Making: Case-making machines are the equipment you need for making a computerized setup.
Clean Room: A type of assembly and packaging service among the facilities of packaging and printing. The purpose of this facility is to get rid of any contamination during different procedures.
Case Sealer: A type of manufacturing machine that you can use for sealing and closing the flaps of any boxes. You can use glue and tape to make sure these packaging boxes are sealed well.
Castors: A type of set of small wheels that you can use for the movement of different objects in the packaging process.
Clay Coat: A thin layer of clay coat that you can coat onto corrugated boxes. This is a method that can help improve the printing surface of this material. One of its common uses is on unbleached kraft paperboard.
Crash Lock: A box style that allows you to lock its base. The main benefit you get from it is no need for tape for its interlocking system.
Cratering: Small and thin spots where you can find bubbles in packaging products that you code with paint or dye.
Crazing: Cracks that can come under a plastic or glass layer.
Creep: A type of deformation that occurs progressively in packaging material. It can be caused by stress; anything or any factor may apply to it.
CSI: A company that can project development and specializes in producing corrugated packaging.
Cushioning: A type of packaging element that allows you to protect fragile products during delivery and transit.
Cycle: The number of times you can get usage from a packaging product, used for reusable packaging containers.
Cushioning Curves: These indicate materials that provide you with different levels of thickness.
Cushioning Bicell: Foam laminate which allows you cushioning properties. At the same time, you get anti-abrasive features with this material.
Creasing: Folding lines that you can find in packaging that allow you to allow the package to be folded and cut as desired.
Terms Starting with D
Damage Burst: Term for packaging containers that may burst or split owing to their exposure to too much pressure.
Declaration: The total amount of shock any packaging product can handle and endure. The main criterion of its measurement is the product should not get damaged by any force applied to it. You can measure it in G force.
Deckle: The width of the board that you can run on a corrugator.
Decorative: Aspect of finish used to identify color and printing of a packaging product.
Demo Case: Cases you can use as a demo during your presentation in the sales meeting or a sales pitch.
Density: The weight of a gas, solid, or liquid that you can measure in the unit of grams per cubic centimeter.
Desiccant: A substance that you can use for drying purposes when you need to try water vapor. The main purpose of this is to decrease and control humidity inside sealed packages. You can use multiple substances for these many of these are calcium oxide.
Design: A packaging design includes drawings and specifications of a packaged product. These specifications help you determine what a box will look like and how it will be constructed as an end product.
Die: A die is a special type of packaging tool that allows you to customize your packaging products. You can create customized dyes to achieve a certain type of box design and other specifications.
Die Cutting: A process that allows you to stamp the cuts and scores that you want to add to a packaging design.
Distributor: Supplier of merchandise or products to a retail seller, who does not use any products but works as a reseller provider.
Dividers: Devices that separate different sections of a container to ensure they get good protection.
Dolly: A small type of device that you can use for moving heavy objects. It has a setup that is fixed on builds and allows you to move heavy objects easily.
Drawing: Creation from an art designer or packaging engineer used for technical purposes.
Drop Test: Test to find out the durability and capabilities of a packaging box.
Dump Bins: A type of point-of-sales packaging that allows you to keep different objects disorderly.
Dunnage: A type of material that you can use to support the protection of packaging against different contaminating factors. Moisture and damage are two factors they allow you to avoid.
Duplex: A type of paperboard you can make out of two layers, commonly used for coating material to gain resistance against water. Often used for pharmaceutical industry paper cups and many other applications.
Double Walled Board: A combination of corrugated material layers to make them one. Using this method allows you to get extra strength for your packaging boxes.
Digitization: A process that allows you to convert data into digital format for packaging and printing purposes.
Dimensions: The length, depth, and height of a packaging box.
Direct Food Contact: Direct food contact is the physical contact of any material with food. There are certain regulations that must be followed if you are packaging a product with direct food contact.
Displays: Type of packaging used to showcase a product or merchandise at the point of sale, which can be made from corrugated material.
Terms Starting with E
Ecommerce: Ecommerce or electronic commerce is a term that is used for selling products online. If you provide packaging or other products through the internet, you are in the ecommerce business.
Ecommerce Packaging: The packaging boxes used for ecommerce purposes are called ecommerce packaging. The purpose of these boxes and packaging is to keep your product safe during transit.
E-Flute: A type of material that allows you good crush resistance. At the same time, it offers you great quality printing.
Egg-Box Foam: A type of form that you can use in packaging. A main feature of this one is being flat from one side and grooved from the other.
Electrostatic: A unit of the decay rate electrostatic charge.
Embossing: A type of effect that allows you to create raised design or lettering on a packaging material surface.
EMC: Acronym that stands for electromagnetic management coupling. You can use this term for a case or product that helps you manage electromagnetic energies in packaging and processes.
Emulsions: A type of topical public quoting which is famous for being water-soluble. At the same time, it would be quarter resistant when it is dry.
End Caps: A type of form question cushioning that allows you protection for the product you pack inside a corrugated box.
Environment Agency: Environment agencies work to improve the regulations set for waste production for packaging.
EPS: Acronym for expandable polystyrene, which is a foam that allows you good thermal insulation and helps you with high impact resistance. You can use it in the construction and packaging industries alike.
ESD: Acronym that stands for electrostatic discharge, which can be a common problem for packaging products.
ESD Anti-static: A type of cortex that allows you to store equipment from entering a packaging box or other product.
ESD Shielding: A type of conductive material that allows you to resist electrostatic charge in packaging.
Estimate: The total amount a company calculates to produce packaging boxes.
Extrusion: A type of method used for producing plastic bottles.
Extrusion Profiles: Term for extrusions of shaped products, which you can get in multiple configurations. These shapes come in box solid and hollow forms.
Ethafoam: A type of semi-rigid packaging that allows you medium-density lightweight. At the same time, it is quite flexible.
Euro Box: A tough and durable storage solution that you can get in standardized sizing. You can get these in warehouse facilities.
Euro Container: This term is used alternately for Euro boxes, as mentioned in the previous section.
Explorer: These are military-grade cases that reproduced in Italy.
Terms Starting with F
Fabrication: The process of manufacturing, often used as a packaging or printing term.
Falling Dart Impact: A traditional method used to evaluate the strength of plastics.
Faraday Cage: A type of enclosure that you can use for blocking electric fields. You can find it in the form of conductive materials. Also, they are available in the form of a mesh of such materials.
Faro: A type of digitization device that allows you to find different computerized versions of a small object used for packaging.
Fatigue: The deterioration of packaging boxes in use. You can use this term for products that can be used repeatedly.
Feasibility Study: Studies to determine if you can get certain results from a particular process, as well as what adjustments to the process are needed to receive the desired results.
FEFCO: Acronym for an organization that sets standards for design patterns for corrugated products in packaging.
Fiber: Fibers are the smallest unit of material that creates a packaging box., also known as molded pulp.
Finish: A type of coating or print that you can use on packaging products. There are multiple benefits of these you can have for your packaging products. For instance, it allows you to get rid of any chances of corrosion.
Foam: A substance that is created through a process of trapping gas pockets inside a solid material. There are different types of these that you can find, like XPS foam and Polyurethane.
Foam Lining: A type of foam liner that you can use inside a case to get protection for your packed products.
Folding Carton: A paperboard product that you can fold, print, and laminate. Also, you can use it by cutting and gluing, and the main purpose of this product is the transportation of products.
Forme: A type of metal cutter that you can use for cardboard scoring. The purpose of this cutting can be die cut finish.
Fulfillment: The use of third-party warehousing for your inventory services for your packaging production.
FSA: A food standard agency determines different standards for shipping food products.
FSDU: A type of display unit you can use for retail packaging products.
Fittings: A range of fixtures that you can add to cases and can be made from plastics and steel.
Flatbed Die Cutting: A process you can use for creasing, cutting, and embossing sheets. You can use this press this die on a material that you can find on a flat surface.
Flat Pack: A type of packaging that you can use for shipping purposes. The main feature of this type is that you can use them as a flat box during such processes.
Flood Coat: Term for when an entire surface will use a dye or color.
Flute Direction: The literal direction you can add inside a corrugated box. You can have two types of directions here, vertical and horizontal. The main feature of these is to get strength for your boxes and other packaging products.
Flute: Paper layer that allows you to get more strength when added to a certain corrugated board. You can get more rigidity for your product with these as well.
Terms Starting with G
Glued: A process that allows you to connect different materials into a box. For instance, different sheets of cardboard can be glued together with wood for strength to your boxes.
G-Force: A type of measurement that becomes the reason for the weight of a product. You can define it as a weight per unit mass.
Gloss: A type of coating that can help you get higher reflection for your packaging boxes. A big feature of this coating is a good color and contrast definition for your boxes.
Terms Starting with H
Hanging Tabs: A type of part that different boxes can carry. The main purpose of this part is to allow you to hang your products packed inside these boxes for display.
Hardigg: Molded equipment cases used to transport fragile and delicate equipment.
HDPE: Acronym for high-density polyethylene. You can use it for blow molding, which allows you resistance against cracks and also provides stiffness.
Heat-Seal: Common method to seal multiple surfaces.
Hermetic Seal: A type of seal you can use when in need of the ability to avoid leaks.
Hinged End Cap: Similar to standard types, however, the main difference is hinged end caps do not involve any bonding feature.
HIPS: Acronym for high-impact polystyrene. The multiple features of this material include cost-effectiveness and resistance against impacts. At the same time, it is quite easy to fabricate this material, making it a low-cost option.
Hot-Melt Adhesive: Term for hot glue, which is famous for being solid at room temperature. On the other hand, you can liquify that by heating it.
HPX Resin: A type of high-performance resin that is a polypropylene copolymer.
Hybrid Pack: A type of packaging that uses both corrugated and rPET materials.
Hand Erect: Term for a packaging type that you can assemble by hand. A common reason to use this type of packaging is the complexity of a packaging box design.
Hand Holes: A type of space you can live inside a box for the purpose of its movement and handling.
Terms Starting with I
Impact Strength: The ability that a box carries against any mechanical shocks.
Imperial: The traditional unit of measurement that you can replace with metric.
Inert: An object that does not cause any reactions.
Injection Molded Case: Term for the production process of certain plastic packaging boxes.
Inkjet Printing: One of the most common types of printing that uses pigmented or dyed printer ink and the creation of images, letters, and other objects.
Inline: A type of die-cutting machinery.
Inline Wheels: A type of equipment that you can use for the purpose of easier movement of larger cases, insert supply chains, and other processes.
In-Mold Labeling: This process allows you to place preprinted labels into the plastic mold. This process is done into the mold before the injection process is done into it.
Inside/Outside View: Inside view refers to the way a package is designed. On the other hand, the printing process of artwork and text is viewed outside the boxes.
Integrated: Plant that creates both the raw material and the products created from those raw materials.
Integral Hinges: Type of one-piece molding is done for cases, and hinges are an important part of this process. You can keep in mind that you can inject two parts of a hinge if you want a cost-effective solution.
Internal Dimensions: The dimensions of a case or box that you get by measuring it from the inside. Just like other box measurements, you keep depth, height, and width in mind during this measurement.
Inter-Stacking Pattern: A mechanism that you can use to stack cases on top of each other with ease.
Inventory: Materials and equipment that are meant for the purpose of reselling.
IP Rating: The effectiveness level of a claim without any closure, measured against foreign objects.
ISO: Acronym that you can use for the international standards organization.
ISO 14001: The environmental management system that allows you to set the framework for this purpose. The system is used for companies to adhere to and ensure environmental management.
ISO 9001 Certified: Certification that a company has met the requirements of this ISO system.
ISTA: Acronym for the international safe transition, which is responsible for setting international safe transit systems. Also used to improve your logistics for your international trade.
Terms Starting with J
Jigsaw Packs: A term referring to cushion packaging that allows for the positioning to be logged alongside one another.
JIT: Acronym for just-in-time inventory system, which is a management strategy that aligns raw-material orders from suppliers directly with production schedules.
Terms Starting with K
K470: A type of lightweight aluminum protective case that is also rugged. This case data test is ATA approved.
Kanban: A Japanese manufacturing system in which you use the scheduling process. Also, you control the inventory system with the supply chain.
KD: Acronym for knocked down, which means that you are sending boxes or cartons in a flat form. This works for the boxes to get stored and shipped.
Kiss Cut: A term that refers to a form of die cutting in which you do not cut the top layer of the material, while leaving the bottom of the material attached.
Kit Skip: A packaging form that sports teams can use to transport their kit, mostly made from aluminum.
Korrvu: A type of packaging that allows you to use films inside corrugated outers to help keep your products safe during transportation.
Kraft: A type of paper colored brown and made from paperboard. The process of its manufacturing has to do with virgin pulp.
Terms Starting with L
Labels: Informative document you can attach to a product which may also include bar codes.
Label Panel: The section of a box where you can add labels to it.
Laser Etching: A type of engraving method in which you can make designs and other elements with the help of lasers.
Layer Pad: Used inside cases to divide layers of stacked products such as cans, bottles and other rigid packaging, used in the rigid layer separation process.
LD: Acronym for low density.
Lead Time: The time that it takes you to get your order from a manufacturer. You can measure it by starting from the time the order has been received till your customer gets the product.
Lid: An attached top that you can use to enclose your contents. This type also has the feature of being removable.
Lightweighting: Reducing the total amount of material used on a particular box for manufacturing to reduce the weight of a box, as well as reduce costs.
Liner: A part of paper material that works as a component of a corrugated board. You can use inner and outer lines that give you higher-quality features. For instance, you can use them for the print finish.
Line-Side: The type of packaging in which you handle containers. The main purpose of these will be your transport components to your assembly lines.
Lithography: The printing of flat services in which you use plates. Also, you can find it as one of the most common and useful types of printing.
Litho Laminated Print: A type of high-quality printer in which you can also add a press with a corrugated board.
Terms Starting with M
Machine Erect: A type of line of packaging which you can use as fully erected by a mechanical machine.
Manufacture: Producing products on a large scale, typically through either the use of machinery and/or manual labor.
Material: A substance of matter from which you can produce a product.
Materials Handling: A system you create for storing and retrieving materials. You can use this system for distribution and manufacturing processes.
Matte Finish: A type of coating that allows you to create a surface that absorbs light. As it is a coating, you can apply it to the surface of a packaging box.
Max Case: A case you can use for military and minding marine industries.
Mini Bag: Bag used for small samples for a serious picture or presentation.
Mission Critical: A certain act or event that is essential for an organization. It can be any act or event you need to perform a certain task.
MLT: Acronym that stands for manufacturing lead time, which is the total time of the production cycle till the finish. There are multiple terms that are used to represent different periods of this total term, including move times, inspection, set up times, and order preparation time.
MM: Acronym for millimeter, which is a type of unit you can use for the measurement of different packaging boxes.
Monomer: A type of chemical that you can use for the purpose of packaging production. The main feature it provides is its reaction with polymer.
MOQ: An acronym for minimum order quantity, which refers to the lowest quantity that a supplier will accept to place an order.
Mold Seam: A vertical groove that you can find at the mold halves, also referred to as a parting line.
Multipoint Gluing: The points where you apply glue to two intricate designs.
Multi Trip: A type of packaging that you can use for multiple trips.
Multi Up: A type of design in which dyes and presses are designed.
Terms Starting with N
NATO Part No: NATO stands for North Atlantic treaty organization, a military alliance. This jargon represents a digit code used for identifying material supplies standards.
N Case: A cost-effective version of smart cases which you can use for presenting and pitching products and their samples.
Nesting Containers: The type of containers you can design with sloped side walls. This allows you to stack them on each other when empty, saving a significant amount of space.
Nomar: A type of abrasion-resistant coating you can use for being water-based and can also be glued.
Terms Starting with O
Offset Litho: An alternative word for mass production printing in which you use the offset method.
Offset Printing: This method uses the transferring from the printing plate onto double blankets. You can also use rollers instead of rubber blankets. It is a popular printing method that provides high quality printing and color labeling.
Ohm: A measurement method that allows you to measure electrical resistance, used for devices and materials.
Operational Temperature: A range of temperatures that protects you for a certain type of packaging or case.
Output: The total number of units certain manufacturing blinds can create in a particular manufacturing cycle.
Outside View: The exterior or outer view of any packaging design.
Overprint: This is the process of printing multiple colors in a way one will be printed on another.
Terms Starting with P
Packaging: Term for placing products in a stock or customized container, bag, or box.
Pack Burst: A type of versatile package design that can contain lubricants. Such packages carry pre measured amounts of these materials.
Pallets: A flat transport structure you can use for supporting products. These can be most commonly used in the form of wood, which also helps you lift and move products.
Pantone: A system you can use for matching colors and for printing inks.
Partitions: A device you can use to create partitions inside a box. You can use interlocking corrugated, cushioning, or other types of boxes.
PE: Acronym for polyethylene material.
Perforations: Small holes made into the side of a material that allows you to open a packaging box more easily.
Performance: Productivity strength features and other noticeable aspects in a packaging process.
Picking Bin: Containers for picking and shipping to the customer.
Pick Face: The front face of the storage that the order picker can see in the warehouse.
Pillow Pack: A box that looks like a miniature cardboard pillow and can pop up into shape by handling. You can use interlocking tabs in them; they are perfect for small products and objects.
Pin-Holding: Small holes you can find in a finish that can occur due to substance. Coating applicators can use multiple options to reduce the chances of such issues.
Plastic Boxes: Any type of plastic box you can manufacture in a wide range of materials you get from plastic.
Platen: A process to achieve flat surfaces by pressing multiple surfaces against each other. There are types of presses that use such a platan process.
Plotter: A device you can use for the cost-effective manufacturing of prototypes. You can also get pre-production samples with them that also give you new manufacturing of specific products.
Plywood: A type of board made from wood carrying 2 layers you can glue together with grain direction altering.
PMS: Acronym for the Pantone matching system, a popular color-matching system used in the printing industry.
Polyethylene: A typically used plastic material that has multiple manufacturing benefits, with three classifications being low, medium, and high.
Polyethylene Foam: A type of closed-shell foam you can use for its resilience against chemicals and the strength it provides.
Polymer: A material that forms large molecules emerging from smaller molecules coming together. There are two types of them; you can get both synthetic and natural types.
Polypropylene: A common material you use for packaging purposes and can provide stress resistance. At the same time, it can be transparent even after production.
Polystyrene: A type of thermoplastic material you can get from the polymerization of styrene. It is non-toxic, and where the resistant features make it special. On the other hand, it can provide you with power and strength.
POS: POS stands for point of sale product displays, which normally showcase products with promotions.
Postal: A type of packaging you can create and use to post items. This means it should serve all the needs you want to fulfill for transportation by posting.
PP: Acronym for polypropylene.
PPE: Acronym for personal protective equipment, which refers to the equipment used to protect team members directly involved in manufacturing.
Press and Pull Catches: Letters used for the purpose of packaging. They can be opened with the push of a button and can stay closed under stress. At the same time, they can bear impact without opening.
Product Amenities: Additional product features.
PU: A thin material you can use for being versatile as a plastic material. It is a flexible form of elastoplastic.
Pulp: Material made from cellulose fibers, wood, and waste paper. You can prepare it by separating cellulose fibers from these materials.
Purge Valve: A valve that allows you to let air flow through a case. But the real feature is that you can stop dust and water from entering this case without stopping the air.
PVA Adhesive: A common type of rubbery and synthetic polymer that you can use as a thermoplastic.
Terms Starting with Q
Quote: A packaging code you can get from a salesperson or an estimator. With this statement, you’ll receive the total price for a specific packaging order.
Terms Starting with R
Rationalization: A process you can use for the purpose of merging similar packaging lines. With these, you can get but if it’s like a smaller inventory and better economies of scale.
Rack Mount Case: A metal framework that allows you to carry electronic equipment.
Rack Unit: A unit that you make for flat cases and portable server cases.
Recyclable: Packaging materials that can be reused, instead of becoming waste or new single-use material.
Reel: A spool or coil that you can use to wind flexible materials around. The benefit of this equipment is that you can easily store and translate these materials with it.
Registration: Locations or marks you can make on print surfaces for better results with the print. It can be quite helpful if you print multiple colors on such a surface.
Resistance: A measurement of how much difficulty an electric current would pass through a conductor.
Rotary Die Cutting: A type of die cutting on a cylinder rotary press, commonly used in line with printing, in which you can use solid and engraved dies. At the same time, you can consider magnetic and adjustable dies.
Rotational Molding: A type of molding process that you can use for plastic materials and has multiple qualities. For instance, it can help you with one-piece hollows and is also stress-free.
RFQ: Acronym that stands for request for quotation that a company or person gets for estimating the costs and to make products.
Reusable: Type of packaging that can be used multiple times before discarding it.
Retail: A method of selling products directly to the public for use purposes and not for reselling or wholesaling.
Royal Mail Sizes: Guidelines to measure the size and weight of different postages, also used for the maximum size of postages you can add.
RSI: This acronym stands for repetitive strain injury that can occur due to repetitive actions.
Run: The total number of products a unit produces in a session.
Retention Pack: A type of packaging that allows you to have cost-effective and simpler protection in the form of protection.
Terms Starting with S
Shadow Board: A type of case insert you can use for an organization station. You can also make them custom forms with foams, and they highlight if a tool is missing or back to the store.
Sheet: A raw material used for packaging and printing.
Sheet Feeders: A type of plant that allows you to work with corrugated sheets with the help of a corrugator.
Shell Case: An alternative commonly used for the purpose of sampling. You can use it instead of a traditional sampling case.
Shielding Layer: A type of conductive layer that you can use for the purpose of blocking electrostatic fields.
Sheet Plant: A company that buys its materials from sheet fitters and cut numbered them into packaging. Such plants typically do not have a corrugator device.
Silk Screening: A printing technique you can use for transferring ink to the printer. There are multiple ways you can use it, like applying it to liners, containers, and other elements.
SKU: Acronym standing for stock-keeping unit or an identification code you can use for an individual or product.
SLA: Acronym for a service level agreement, which is a contract that a provider tells about the responsibilities of the supplier, as well as vice versa.
Sleeve: A type of paperboard that you can customize with shape and style. You can make it in a way that slides over another one to provide you with decoration and beauty.
Smart Case: A type of packaging case you can use to show products for a sales pitch or a business meeting.
Sourcing: A term encompassing all functions used for raw materials. You can also consider the collection, processing, and recycling of these processes.
Spec Number: A five-digit number that you can use for a certain design.
SPRC: The total time that a production unit can use to create a certain amount of products.
SSE: Acronym for static-safe environments that work by distributing certain conductive products.
SSI Schaefer: A manufacturer of warehouse logistics systems shelving storage equipment, and many other similar products.
Stack Height: Regulations that must be maintained to ensure that you stack packaging safely.
Stacking Corner: The type of strong plastic corner that you can add to a case or a package to make it more steady and safe. So, the main purpose of it is during stacking.
Standard 300: A standard age of presentation cases of shell type.
Starpack: An organization in the packaging and printing industry that recognizes innovations in technology and design packaging.
Stereo: A type of flexible plate that you use for printing, so it’s even easier, like the flexographic technique.
Stillage: A type of brake or pilot you can use to hold multiple items. A common use of these is lineside assembly applications.
Static Dissipative: A form or material you can use to dissipate static charges. These boxes help protect any item within these boxes against any such charges.
Spool: A type of cylinder that allows you to wind flexible materials around.
Single Wall: A certain type of box you can use for packaging purposes, which you can use with two materials. You can have fluted paper and then two materials that you can bond on any of the two sides of this material.
Simulated Rainfall: A test used in the UK for checking the protection of a packaging box.
Single Pass Printing: A single-pass printer allows you the production of four-color printing and monochrome data in one pass.
Single Source: A method of providing supplies to customers from one source. You can save costs with these and make management easier and better.
Single-Up: A type of rotary die cutter you can use to cut products in one particular shape.
Sheet Plant Association: An association that works on the motion of best practices in their member companies.
Shelf Life: The total time during the age of the product can be usable after production. Packaging is one of the best methods to improve the shelf life of your products.
Shelf Ready Packaging: A type of packaging that allows for easy assembly and display of your product.
Sampling: The process of creating a prototype that you can use to get customer approval. All of its features must be like the products you will create. It is a process of creating a sample to show your customer what the end product will look like.
Seams: Encompasses various techniques used to keep a package together. The methods you use in this technique are tapping, stitching, and gluing. For instance, you may use a corrugated board to make it bigger and stronger.
Strapping: The process you can use for strapping and combining straps. You can try reinforcing these for stability for certain packaging products.
Stratocell: A type of low-cost polyethylene foam that is used for packaging. You can try using it for the inner cushioning of a packaging box.
Style: A style guide can be used for the purpose of box designs that the European federation has set.
Supazote: A type of cross-linked ethylene copolymer format that you can use for its extremely soft feel.
Supply Chain: A network that you create between different companies to handle and produce like any product.
Suspension Pack: A type of check that protects your products during transit. Its mechanism of making products suspended between two layers allows you to get rid of impact.
Sustainability: Processes and products that reduce the chances of environmental harm and promote eco-friendliness.
Terms Starting with T
Tamper Resistant Seal: A type of seal that cannot be opened without clear evidence of tampering. When you try to open such a seal or gap, it will be partially destroyed, showing the abundance of tempering with the product.
Tamper Evident Band: A part of caps and seals that allows you to determine if a product has been tempered. This way, you can reveal if any product has been tampered with or not. Once you open a cab, this part would be destroyed to provide evidence of this activity.
Tear Strip: A type of plastic film that you can apply to the inside of a package.
Tear Tab: An extension of a tearing strip that you can find on a package or a bottle. Its purpose is to provide easy grasping of the packaging.
Technobag: A type of presentation bag made from polypropylene in Germany. Often considered for project production with injection molding, as they have a single wall.
Test Liner: Manufacture a type of recycled liner board as a sheet of fibers. The big feature of this one is that all the fibers in this one are similar. Its outer layer is better quality cycle fiber, called multiply or duplex.
Thermoforming: A type of manufacturing process in which you use vacuuming or pressuring. There are a number of industries you can use it for, like product displays, clamshells, and food packaging needs.
Triboelectric Charge: A type of charge that can be produced by different materials coming together.
Tri-Wall: The triple-floated corrugated board has the ability to provide flexibility and strength. At the same time, it has amazing eco-friendliness that makes it quite preferable.
Tubes: Equipment used for the purpose of corrugated tubes for multiple reasons. Commonly you can find these alongside end caps.
Turkey Lock: A style of box that comes with a full overlap base, which does not require tapping.
Tool Control: A type of tool organization insert that you can use for cases. You can get its highlight when you’re missing different colored foams.
Tongue and Groove Seal: A type of extended group that you can operate even on mind mirror image concepts, with the ability of a titled enclosure.
Travel Skips: Large aluminum cases used to transport sports kits and equipment.
Trays: Packaging solutions commonly used for samples and other product elements.
Tote: A type of plastic container that you can stack one upon each other.
Transit: The process by which you transport products from one place to another for shipping.
Transit Damage: Any damage to a product that may occur during transportation.
Terms Starting with U
Ultrasonic Welding: A type of industrial building technique that allows you to create certain types of materials. You can use ultrasonic high-frequency vibrations for this purpose. It allows you to create a solid-state world that you can use for plastics.
Unit Cost: The cost for manufacturing a particular product. Multiple types of costs exist, such as overhead costs, labor costs, among others.
Terms Starting with V
Varnish: A type of ink that can be shortened or glossy. At the same time, it can be made and helps improve the beauty of a product, as well as increased product protection.
VCI: Acronym that stands for vapor corrosion inhibitor. The coating allows you to get protection against corrosion. It works both passively and actively to provide this protection.
Vector: A type of graphic that is made up of paths and defines points from start to end. These images are made from multiple dots, allowing you to scale them up without any quality loss.
Vibration: Factors such as loose cargo that can damage packaging products and goods packed inside.
Vibration Sweep: A vibration that travels from one frequency to another. You can use this method for protective cases.
Virgin Material: A term of approval that a material has not been processed in any way except in its manufacturing process.
VMI: Acronym that stands for vendor management inventory, used in stock management to determine the appropriate packaging levels.
Void Fill: A type that you can use to protect a certain product inside a packaging box. You can get it from certain materials that fill the whole box except the product packed inside.
Volume: The total number of units a manufacturer can produce in a certain amount of time.
Volume Resistivity: The ability that a material contains to resist the flow of current.
Vortex Pressure Relief Valve: A type of valve that can help adjust air pressure without letting in any water, and it does it automatically.
Terms Starting with W
Waterjet Cutting: A type of equipment that allows you to cut materials with the help of high water pressure.
Weight: The density of a material used for packaging purposes.
Warehousing: The storage of parts and components that you can use for the purpose of packaging and printing processes.
Wastage: The components or packaging boxes that do not meet your quality standards and can be discarded.
Terms Starting with X
Xtrabag: A type of case that makes you lightweight and is made of plastic.
Terms Starting with Y
Yield Value: The actual amount of force needed to start an ink flowing.
Terms Starting with Z
Zarges: Manufacturer of a range of aluminum shipping cases and containers.
FAQs
What are the most common examples of packaging?
When it comes to the examples of products in this industry, there are multiple products you can have. For instance, there are products like:
What are the most common types of packaging boxes in the packaging industry?
The type of box ultimately depends on the unique products and custom specifications. In general, the most common types of boxes tend to be mailer boxes, candle boxes, product boxes, ecommerce boxes, and other retail packaging boxes.
What is packaging, and why does it matter for products in different industries?
Packaging is any type of product cover that needs protection against environmental factors that can cause issues.
What is the importance of packaging abbreviations?
When it comes to the terminologies used in the packaging industry, abbreviations play an important role. The better you understand printing jargon, the more impactful your collaborative packaging process and output can be.
What are the most common food packaging types?
When it comes to the food packaging industry, there are multiple products that are essential. For example, cake boxes, cookie boxes, and other bakery packaging are quite commonly utilized.
What does retail packaging mean?
When it comes to what retail packaging means, it is simple that any type of box for selling to end consumers must be a retail packaging box.
What does bulk packaging mean?
Bulk packaging is a type of packaging that allows for scalability in box quantities, as well as more cost-efficient unit prices due to increased order size.
Refine Packaging: Your Ultimate Custom Packaging Partner
So, you’re armed and ready with all of the packaging terminology that can help you grow as a packaging professional. Now it’s time to start the packaging production process!
Refine Packaging can assist from conceptualization to mass box production. We aim to provide as many options as possible and simplify the process so you can see your idea materialize in the shortest time possible.
Select from our array of custom box industries and products, or let us know your concept so our designers can work with you. We use various printing techniques and offer 2D and 3D mockups of your packaging. Our team can send you a sample so you can verify if the prototype matches your vision.
But don’t just take our word for it—discover how the Refine Packaging process has delivered successful customer stories for 1,000s of satisfied brands and their clientele. Contact us for a free quote today, and our packaging specialist will connect with you shortly.
Ready to think outside the box? Let's get started!
Get in touch with a custom packaging specialist now for a free consultation and instant price quote.


.svg)



























Share